Exposing MCPs on the Public Internet
Control which MCP servers are visible to external callers (e.g., ChatGPT, Claude Desktop) vs. internal-only callers. This is useful when you want a subset of your MCP servers available publicly while keeping sensitive servers restricted to your private network.
Overview
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Description | IP-based access control for MCP servers — external callers only see servers marked as public |
| Setting | available_on_public_internet on each MCP server |
| Network Config | mcp_internal_ip_ranges in general_settings |
| Supported Clients | ChatGPT, Claude Desktop, Cursor, OpenAI API, or any MCP client |
How It Works
When a request arrives at LiteLLM's MCP endpoints, LiteLLM checks the caller's IP address to determine whether they are an internal or external caller:
- Extract the client IP from the incoming request (supports
X-Forwarded-Forwhen configured behind a reverse proxy). - Classify the IP as internal or external by checking it against the configured private IP ranges (defaults to RFC 1918:
10.0.0.0/8,172.16.0.0/12,192.168.0.0/16,127.0.0.0/8). - Filter the server list:
- Internal callers see all MCP servers (public and private).
- External callers only see servers with
available_on_public_internet: true.
This filtering is applied at every MCP access point: the MCP registry, tool listing, tool calling, dynamic server routes, and OAuth discovery endpoints.
Walkthrough
This walkthrough covers two flows:
- Adding a public MCP server (DeepWiki) and connecting to it from ChatGPT
- Making an existing server private (Exa) and verifying ChatGPT no longer sees it
Flow 1: Add a Public MCP Server (DeepWiki)
DeepWiki is a free MCP server — a good candidate to expose publicly so AI gateway users can access it from ChatGPT.
Step 1: Create the MCP Server
Navigate to the MCP Servers page and click "+ Add New MCP Server".
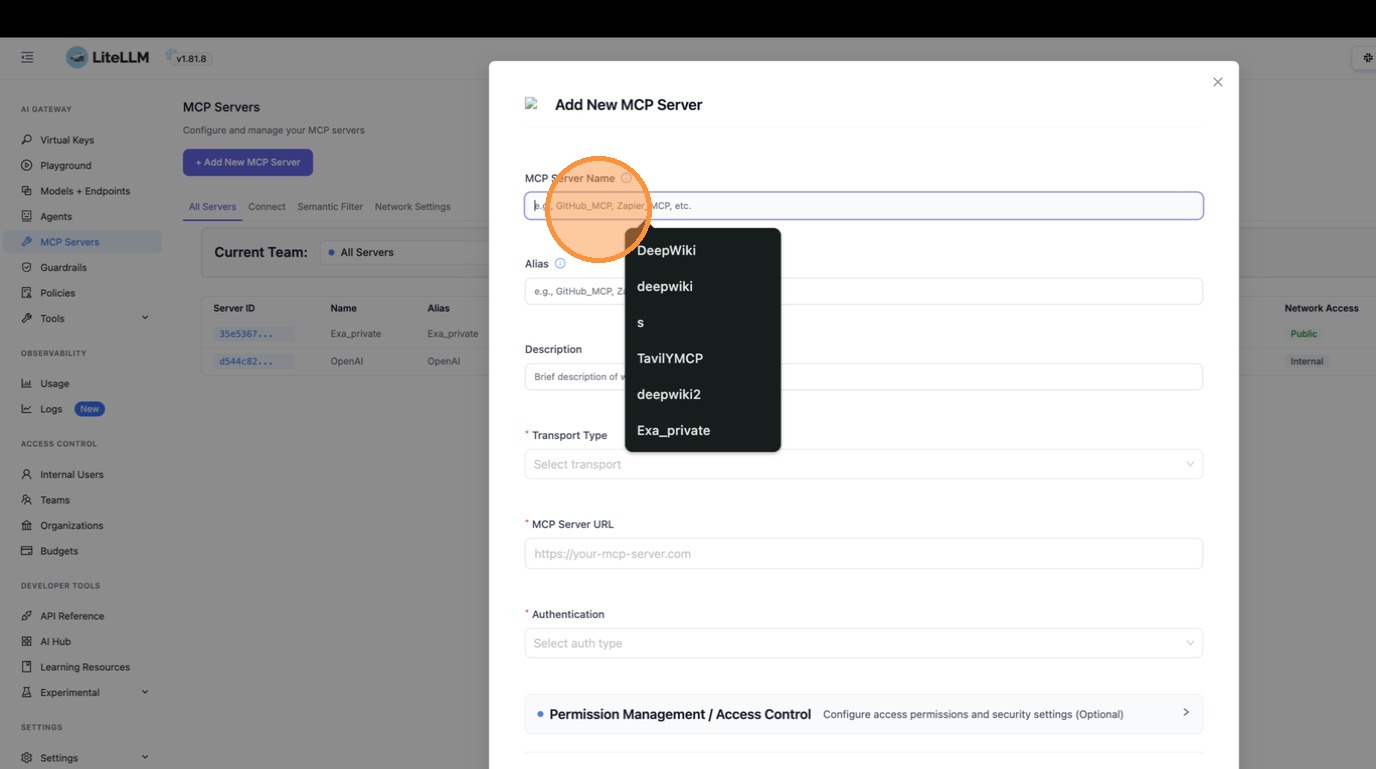
The create dialog opens. Enter "DeepWiki" as the server name.
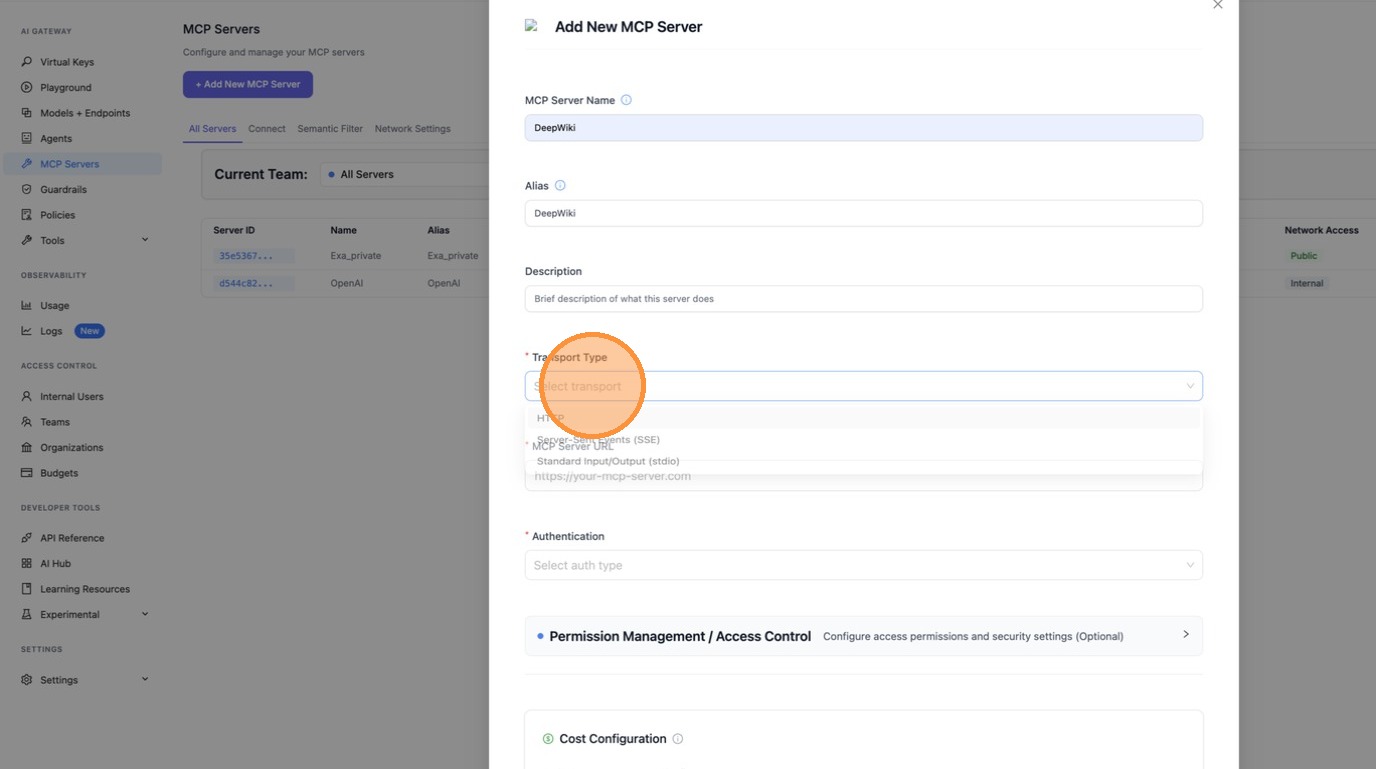
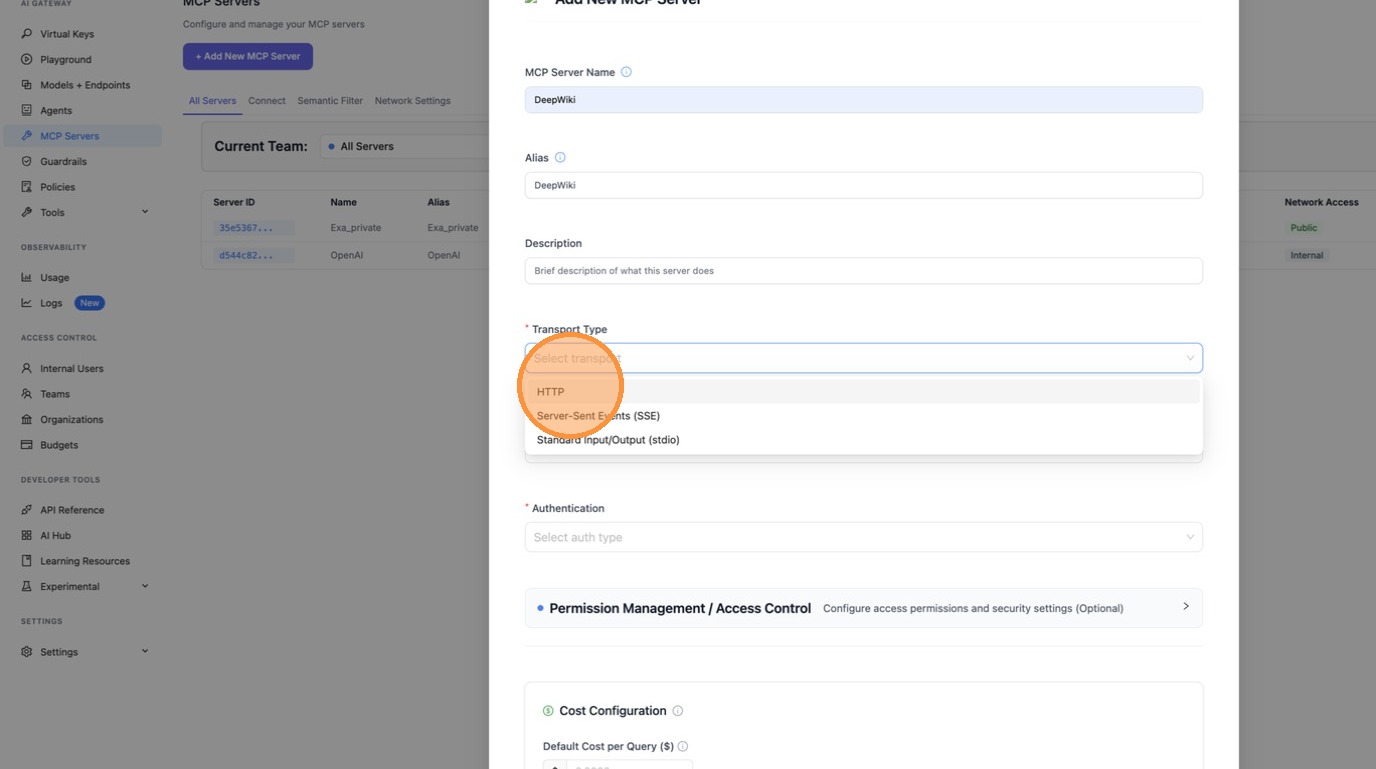
For the transport type dropdown, select HTTP since DeepWiki uses the Streamable HTTP transport.
Now scroll down to the MCP Server URL field.
Enter the DeepWiki MCP URL: https://mcp.deepwiki.com/mcp.
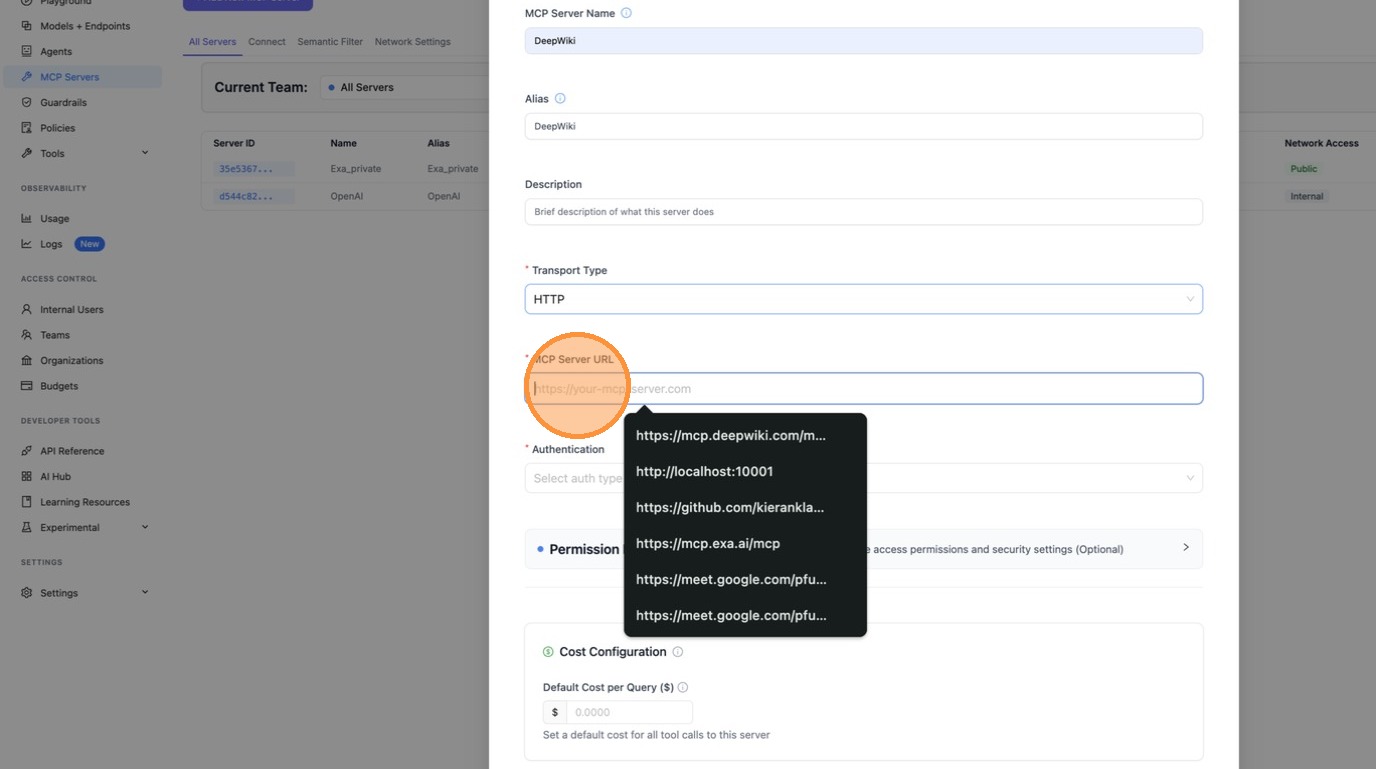
With the name, transport, and URL filled in, the basic server configuration is complete.
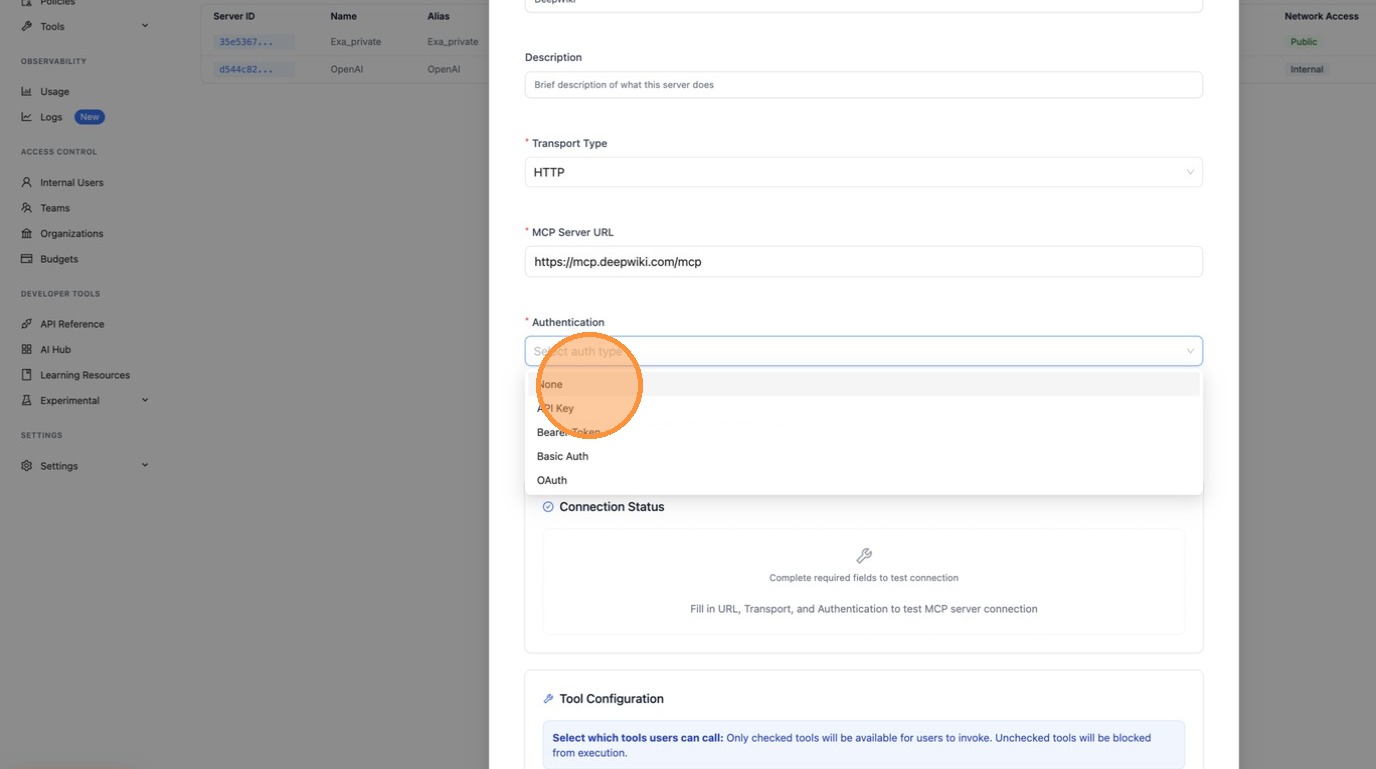
Step 2: Enable "Available on Public Internet"
Before creating, scroll down and expand the Permission Management / Access Control section. This is where you control who can see this server.
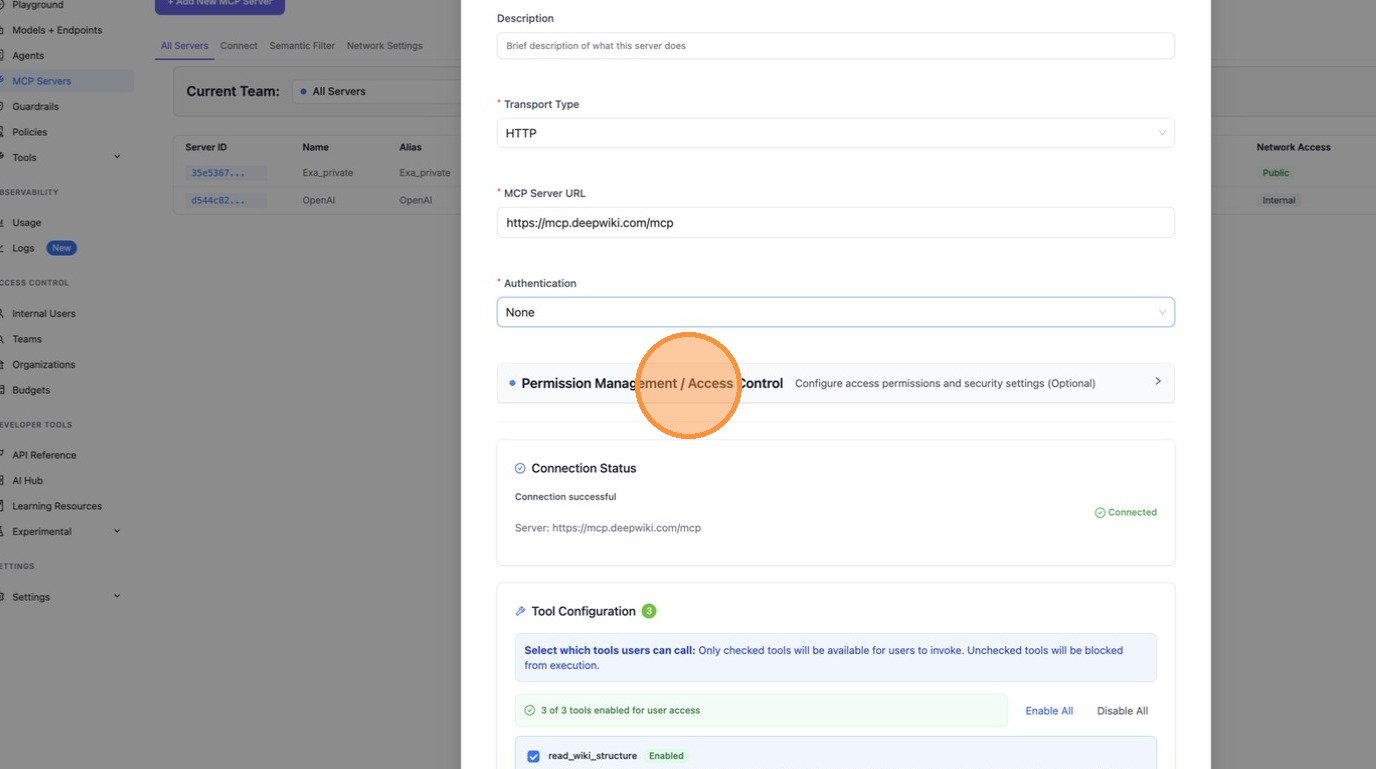
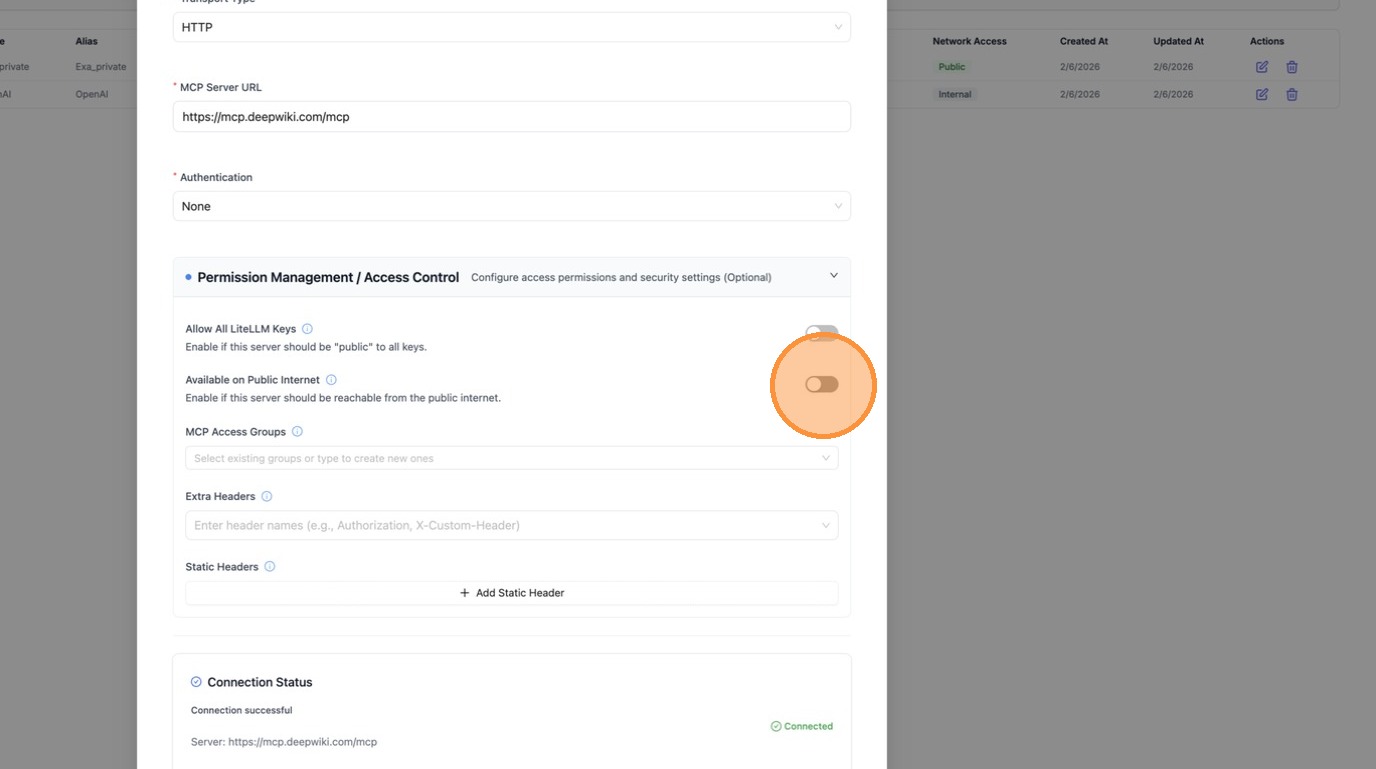
Toggle "Available on Public Internet" on. This is the key setting — it tells LiteLLM that external callers (like ChatGPT connecting from the public internet) should be able to discover and use this server.
With the toggle enabled, click "Create" to save the server.
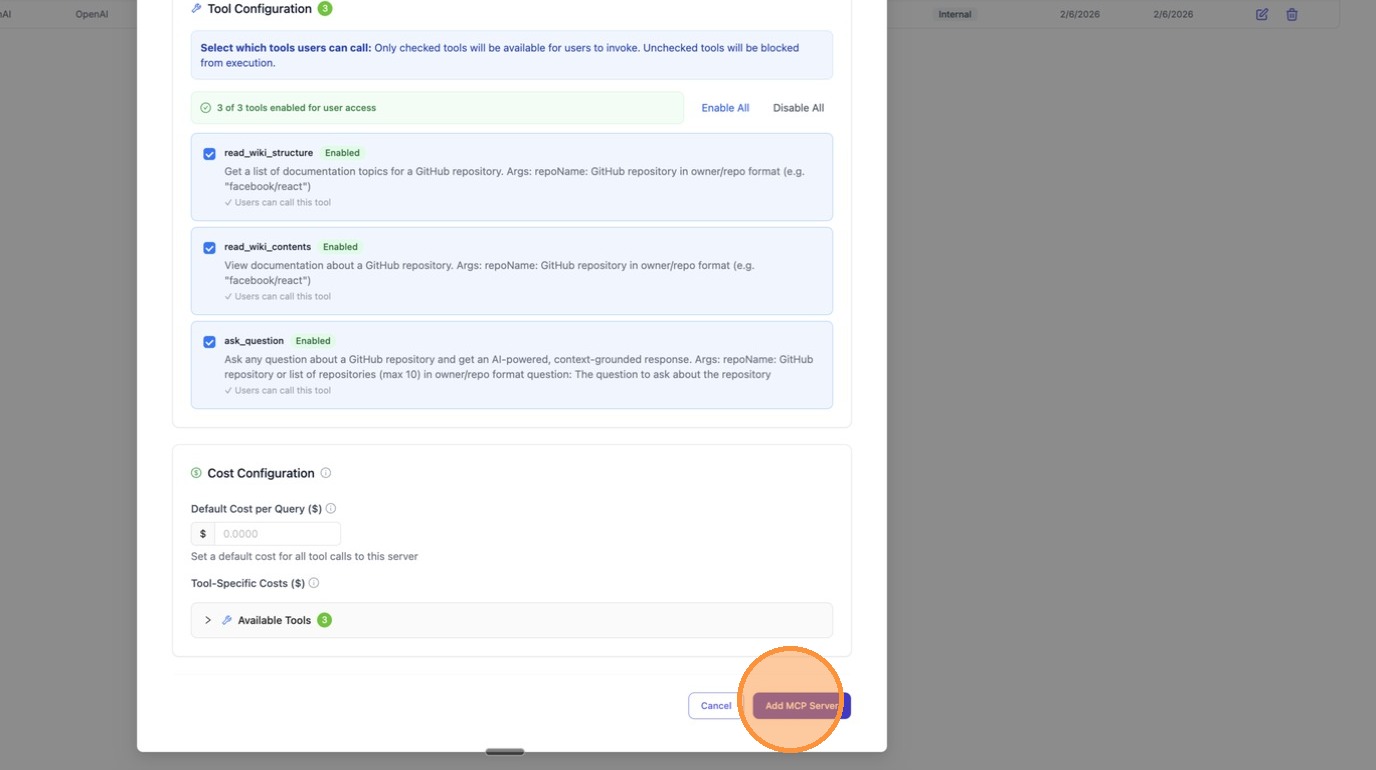
Step 3: Connect from ChatGPT
Now let's verify it works. Open ChatGPT and look for the MCP server icon to add a new connection. The endpoint to use is <your-litellm-url>/mcp.
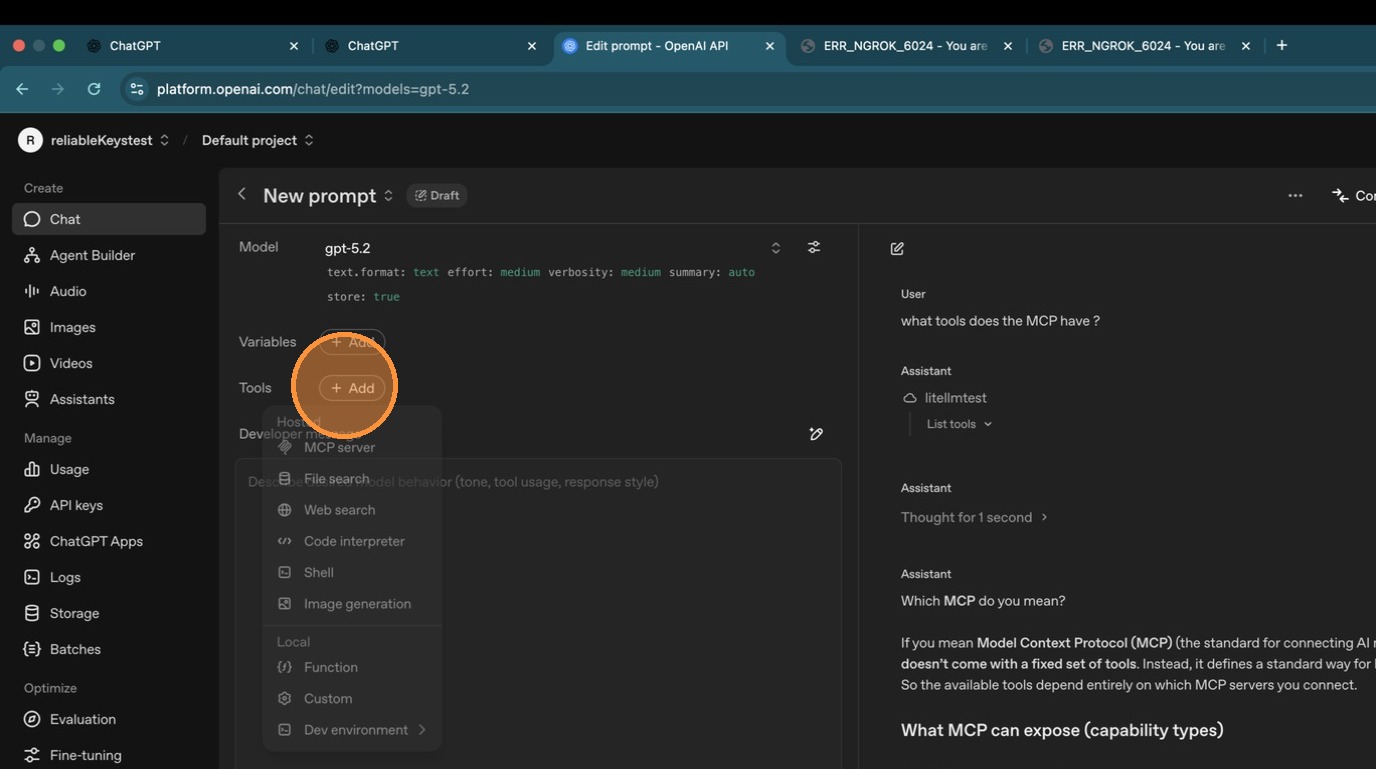
In the dropdown, select "Add an MCP server" to configure a new connection.
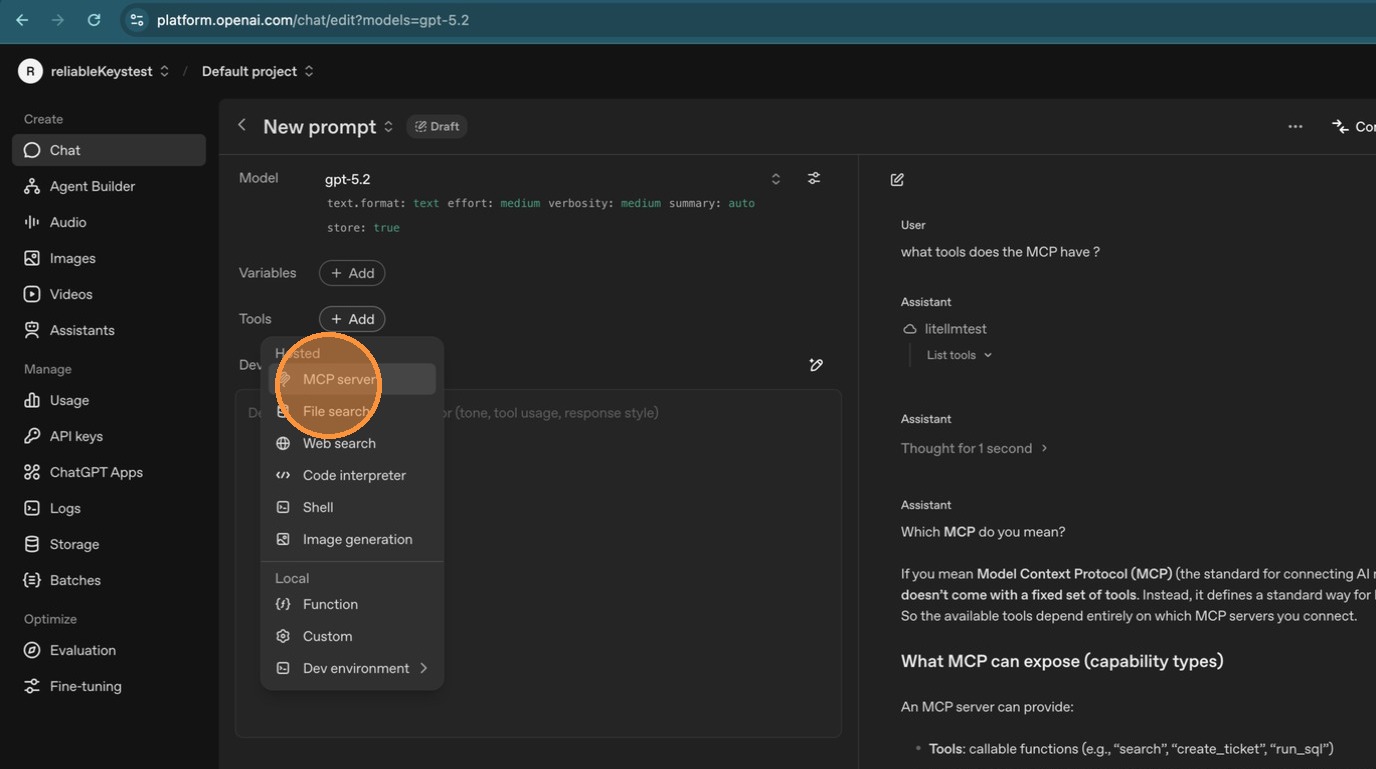
ChatGPT asks for a server label. Give it a recognizable name like "LiteLLM".
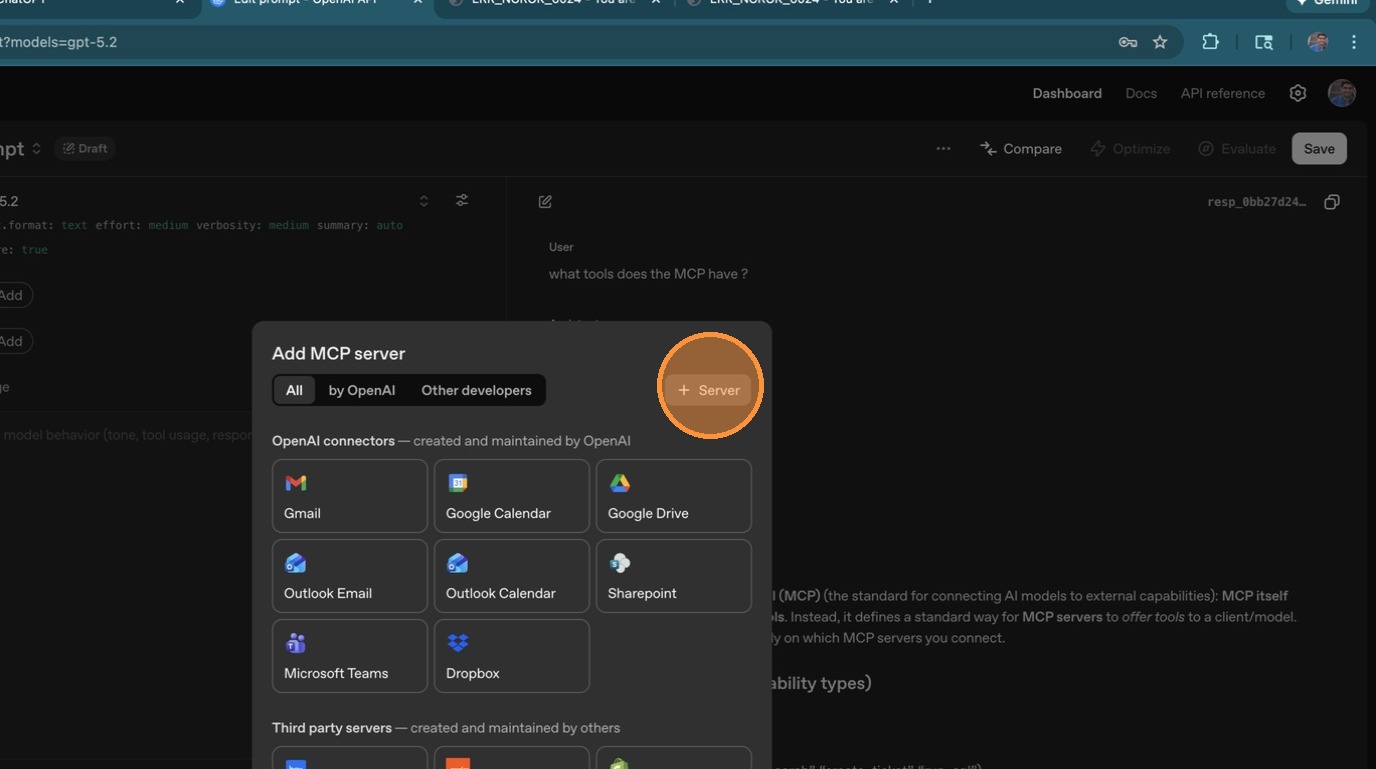
Next, enter the Server URL. This should be your LiteLLM proxy's MCP endpoint — <your-litellm-url>/mcp.
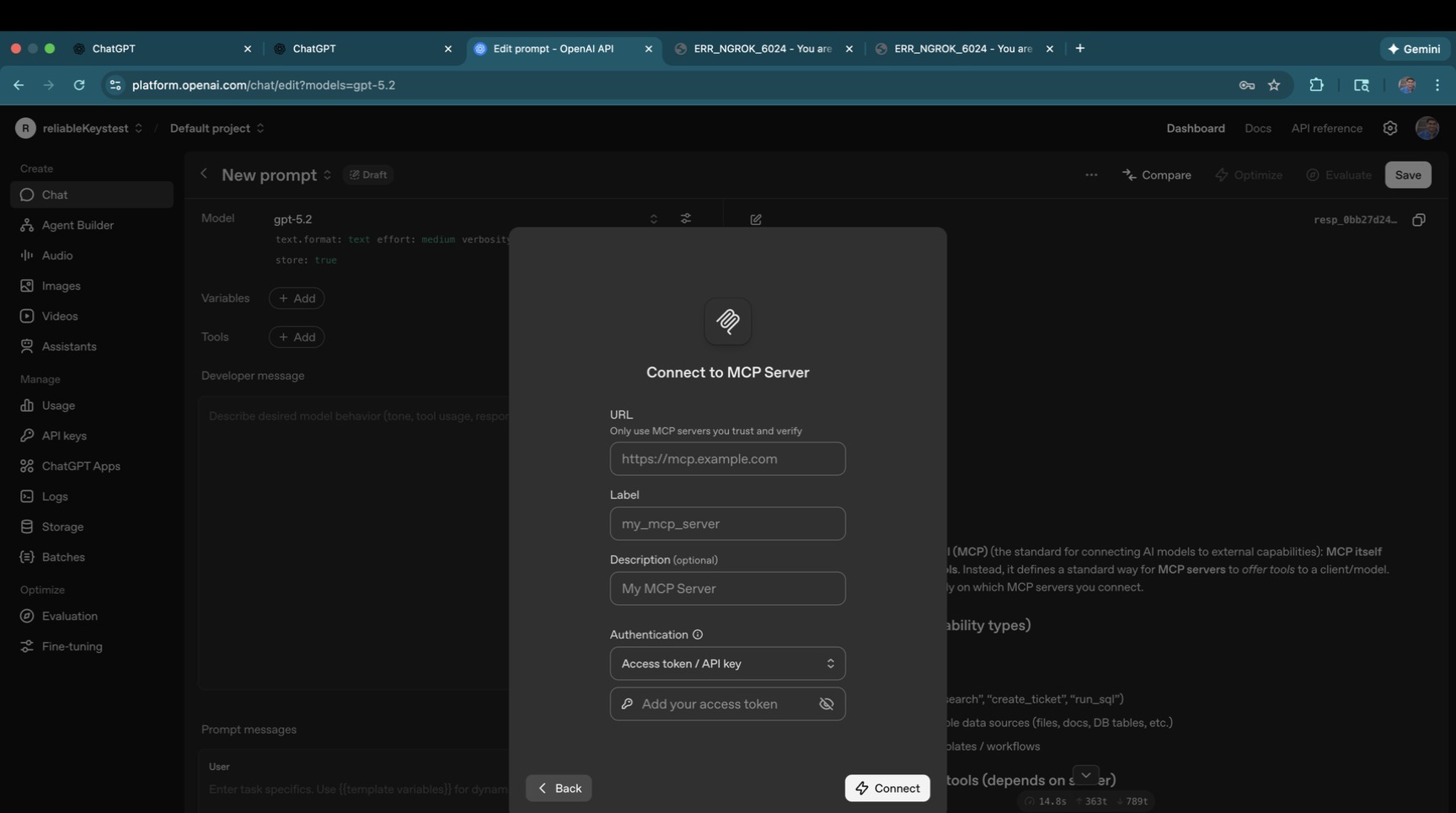
Paste your LiteLLM URL and confirm it looks correct.
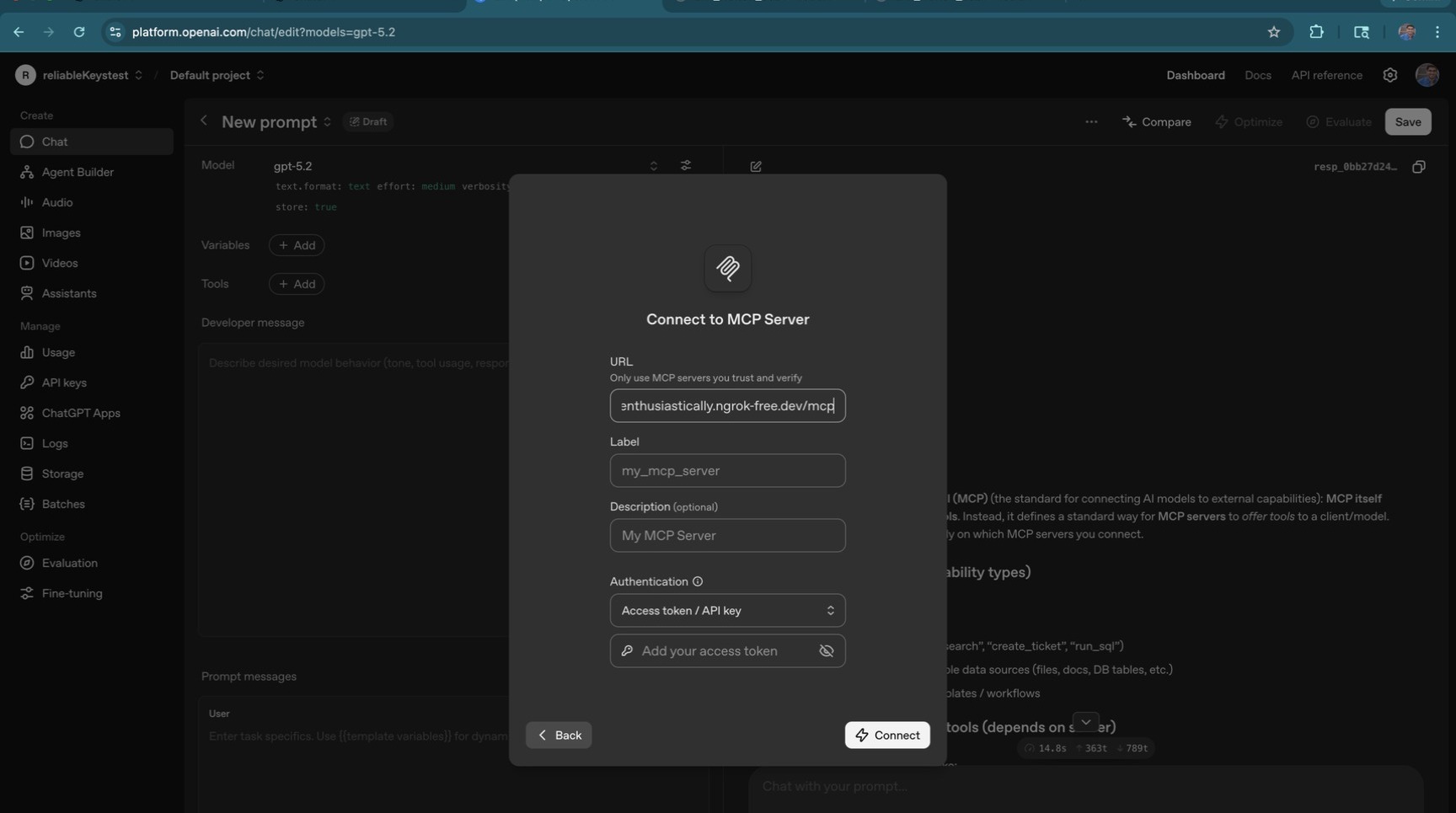
ChatGPT also needs authentication. Enter your LiteLLM API key in the authentication field so it can connect to the proxy.
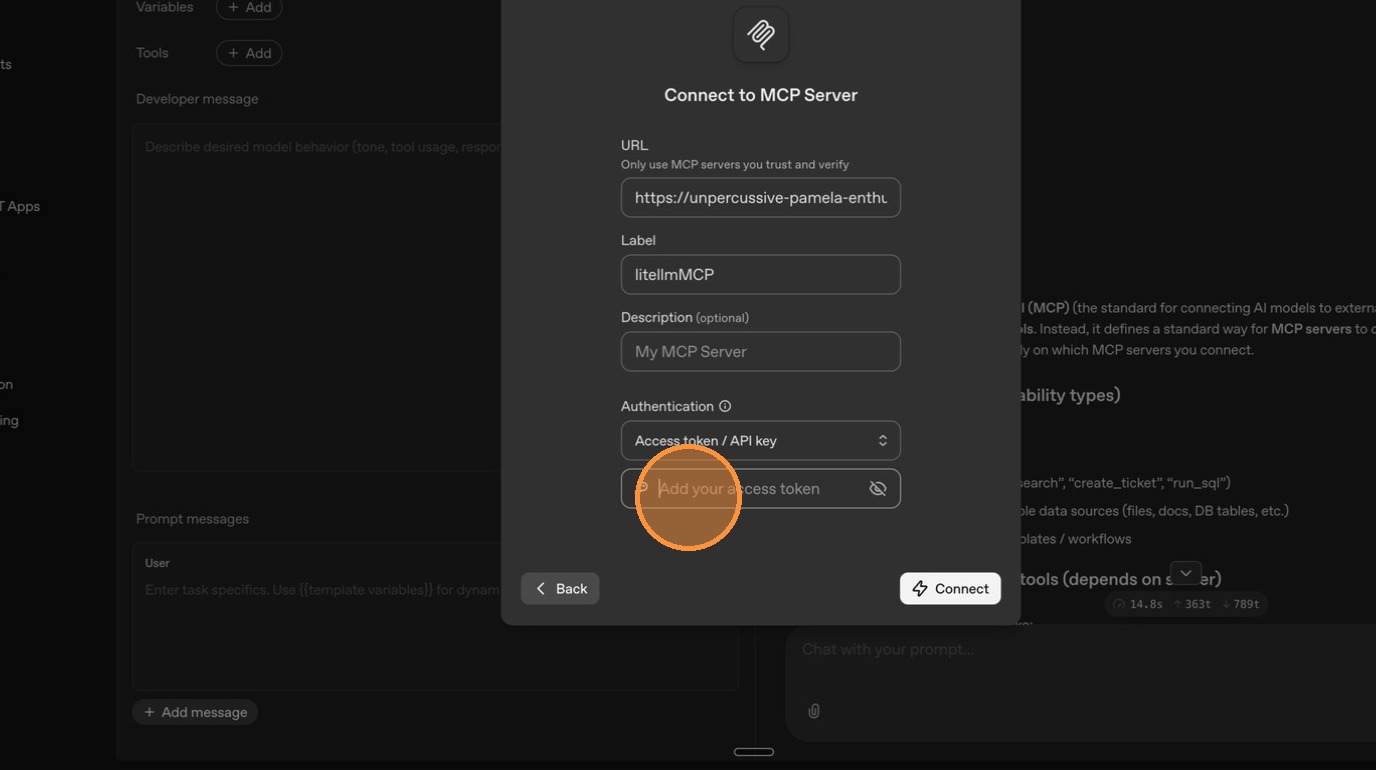
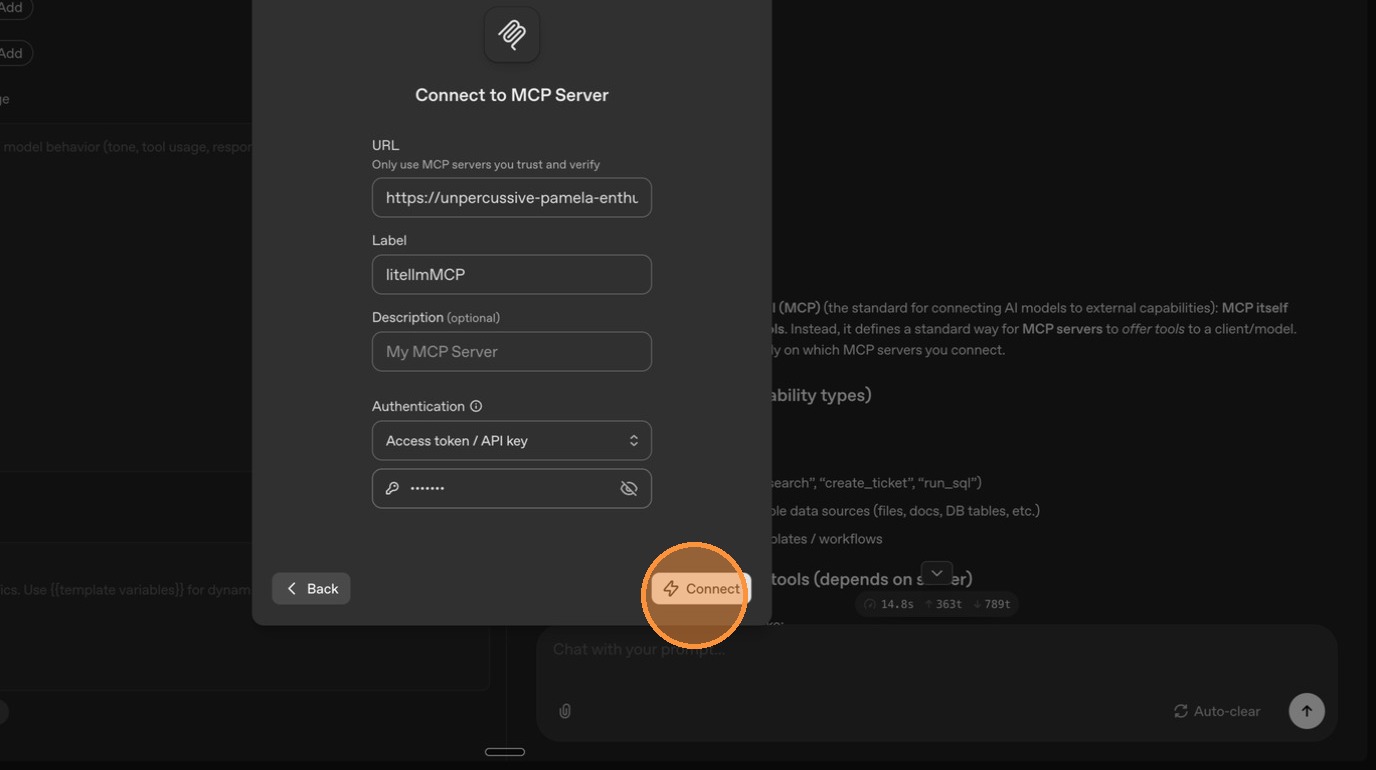
Click "Connect" to establish the connection.
ChatGPT connects and shows the available tools. Since both DeepWiki and Exa are currently marked as public, ChatGPT can see tools from both servers.
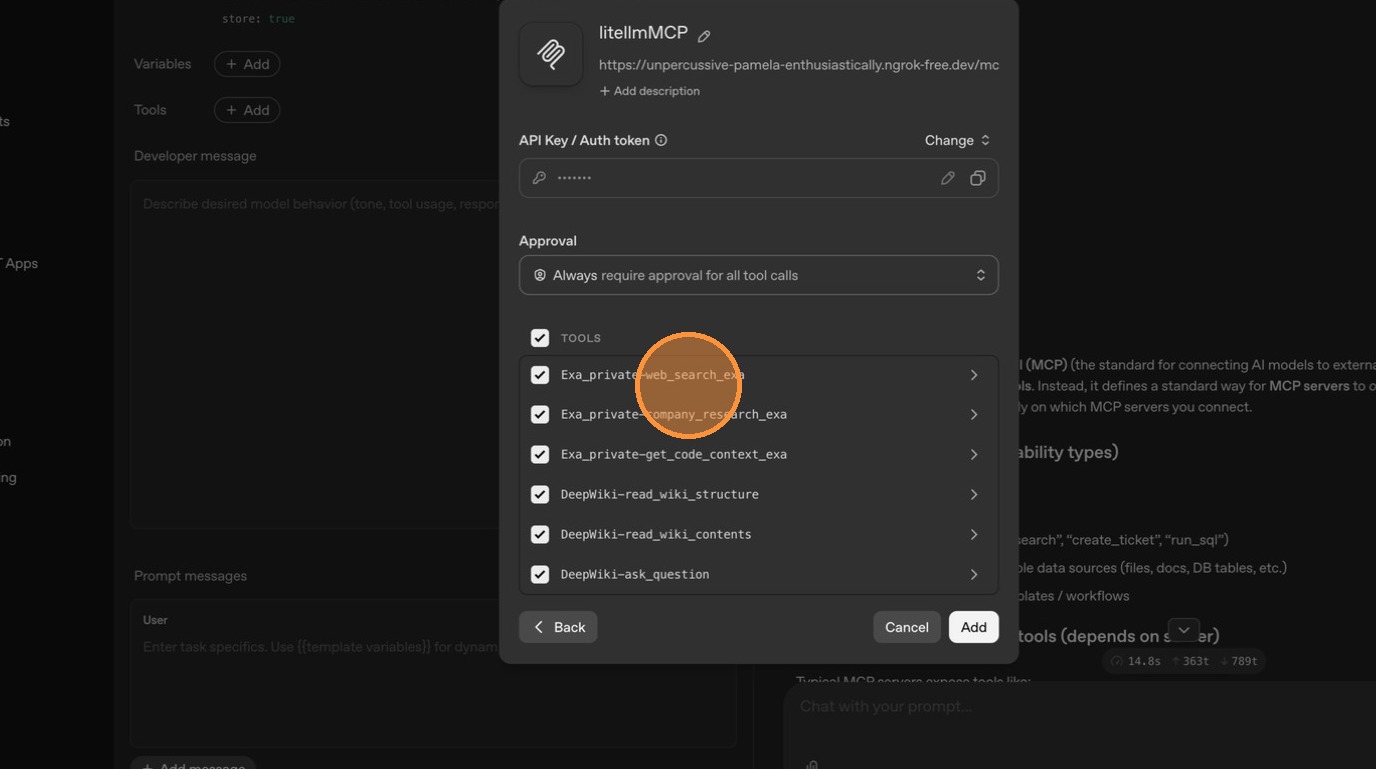
Flow 2: Make an Existing Server Private (Exa)
Now let's do the reverse — take an existing MCP server (Exa) that's currently public and restrict it to internal access only. After this change, ChatGPT should no longer see Exa's tools.
Step 1: Edit the Server
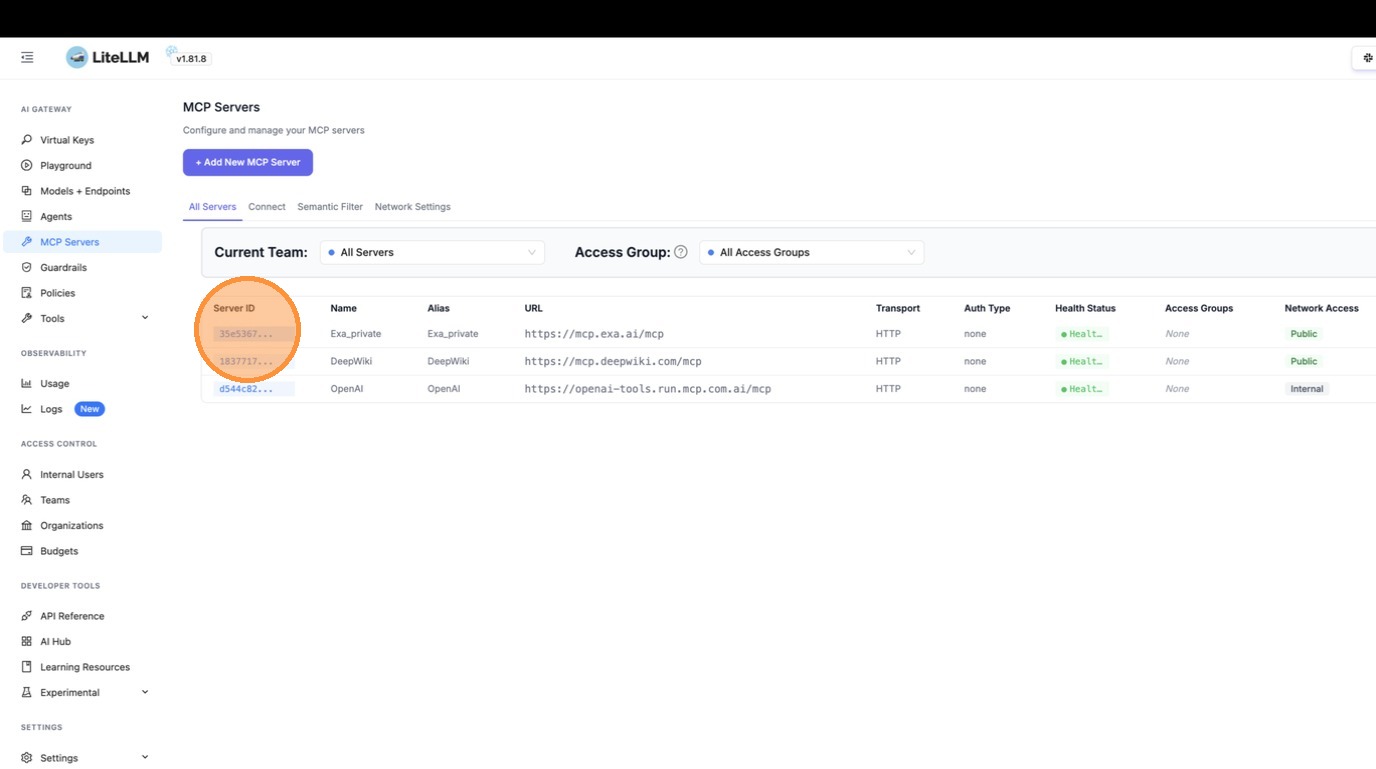
Go to the MCP Servers table and click on the Exa server to open its detail view.
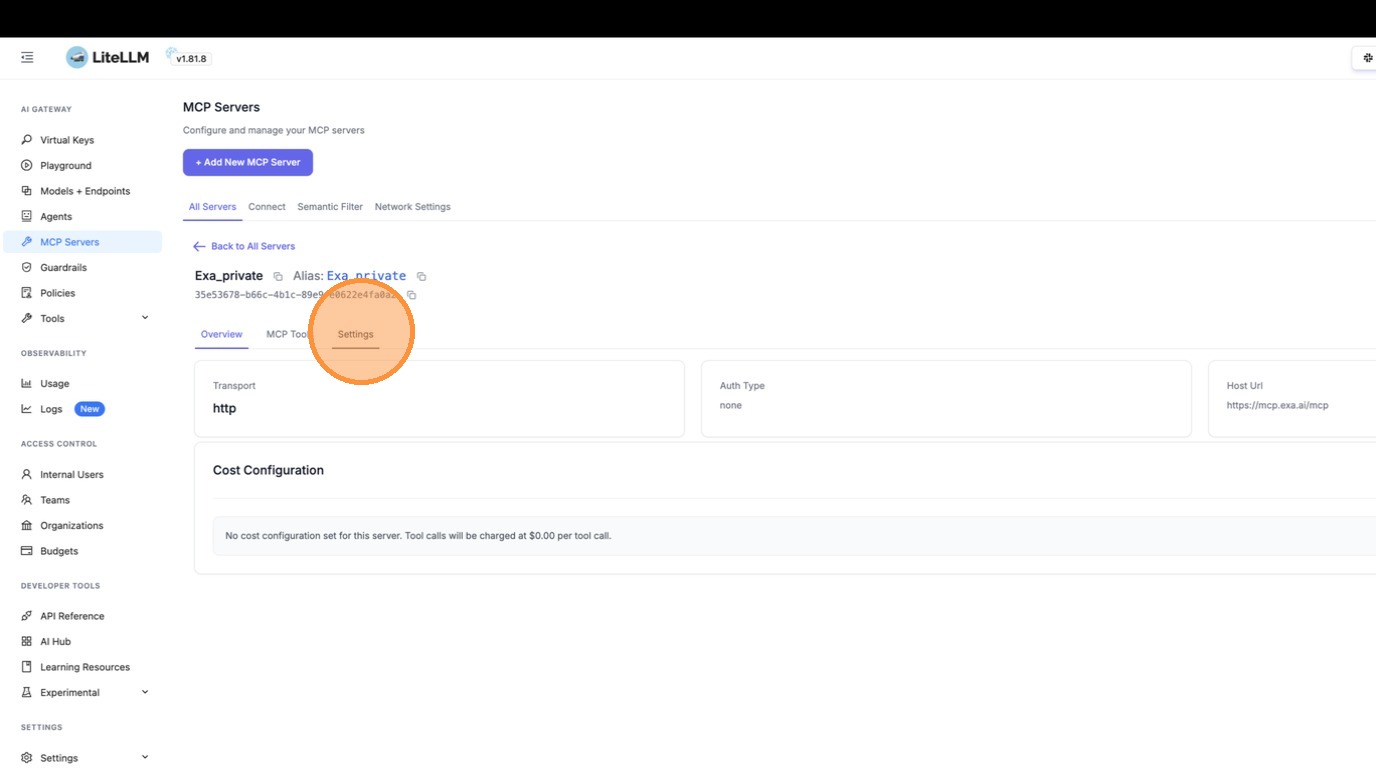
Switch to the "Settings" tab to access the edit form.
The edit form loads with Exa's current configuration.
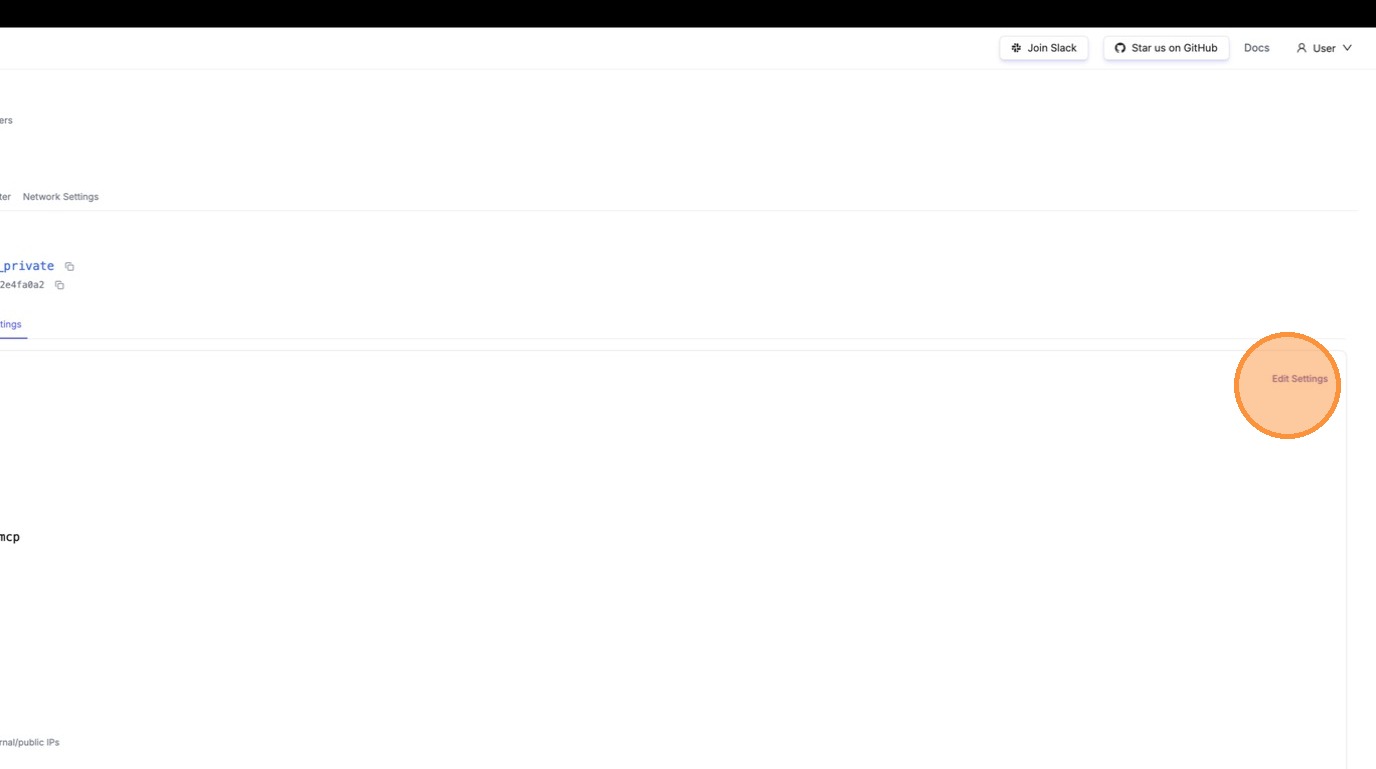
Step 2: Toggle Off "Available on Public Internet"
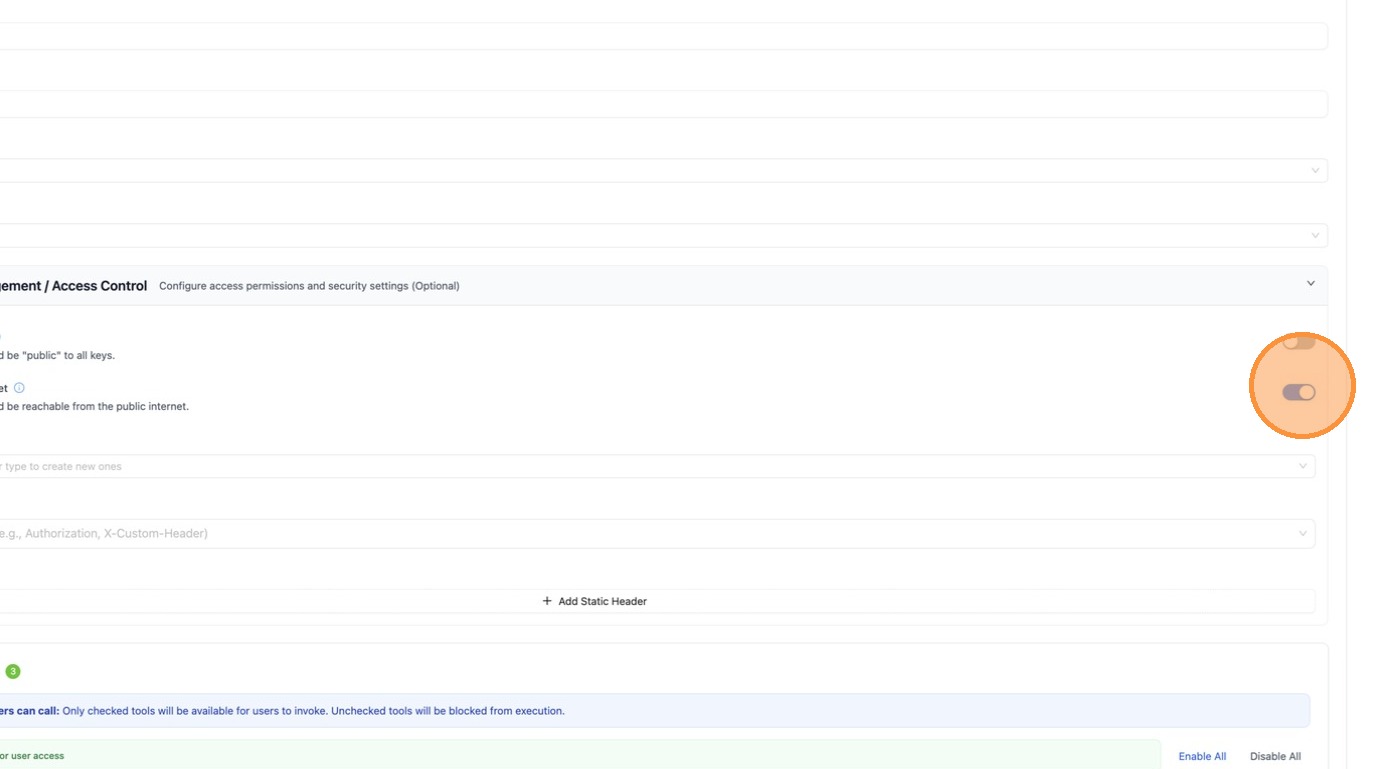
Scroll down and expand the Permission Management / Access Control section to find the public internet toggle.
Toggle "Available on Public Internet" off. This will hide Exa from any caller outside your private network.
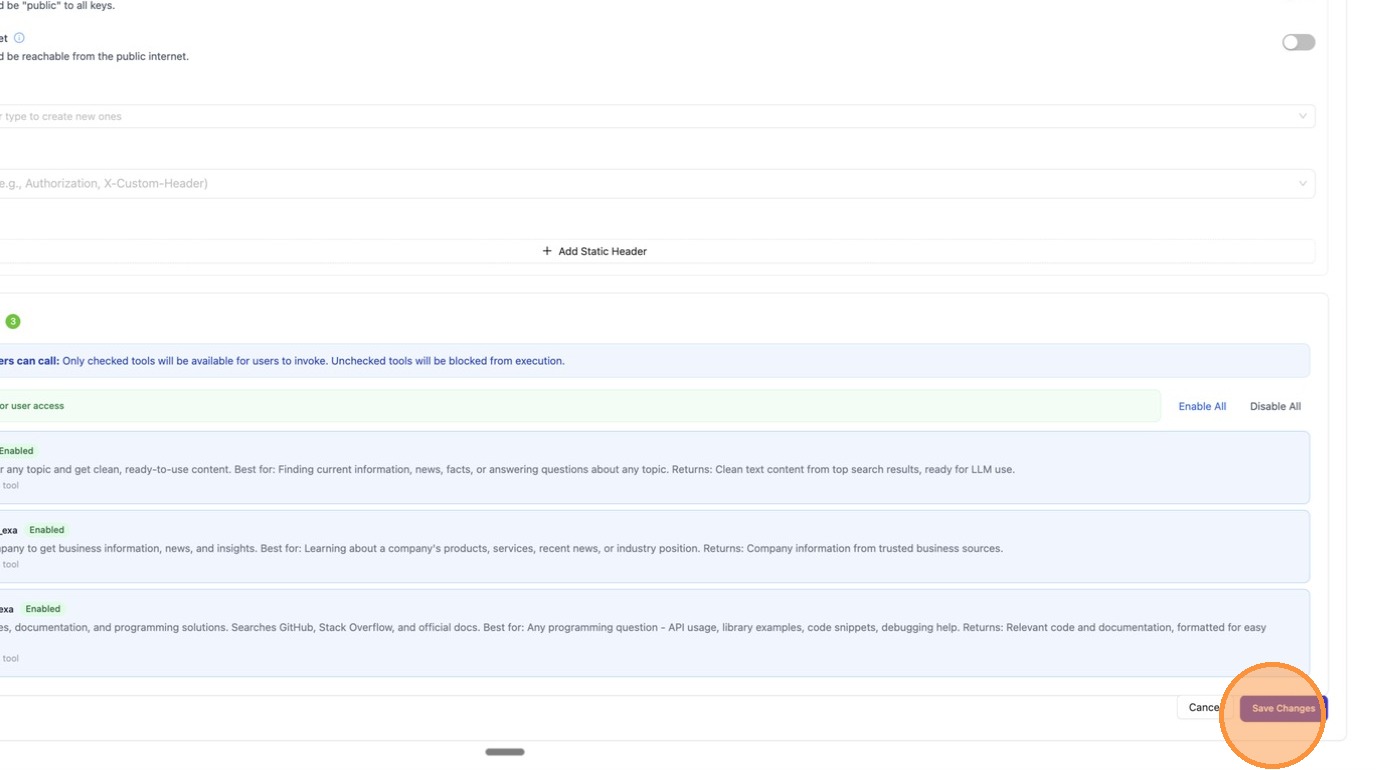
Click "Save Changes" to apply. The change takes effect immediately — no proxy restart needed.
Step 3: Verify in ChatGPT
Go back to ChatGPT to confirm Exa is no longer visible. You'll need to reconnect for ChatGPT to re-fetch the tool list.
Open the MCP server settings and select to add or reconnect a server.
Enter the same LiteLLM MCP URL as before.
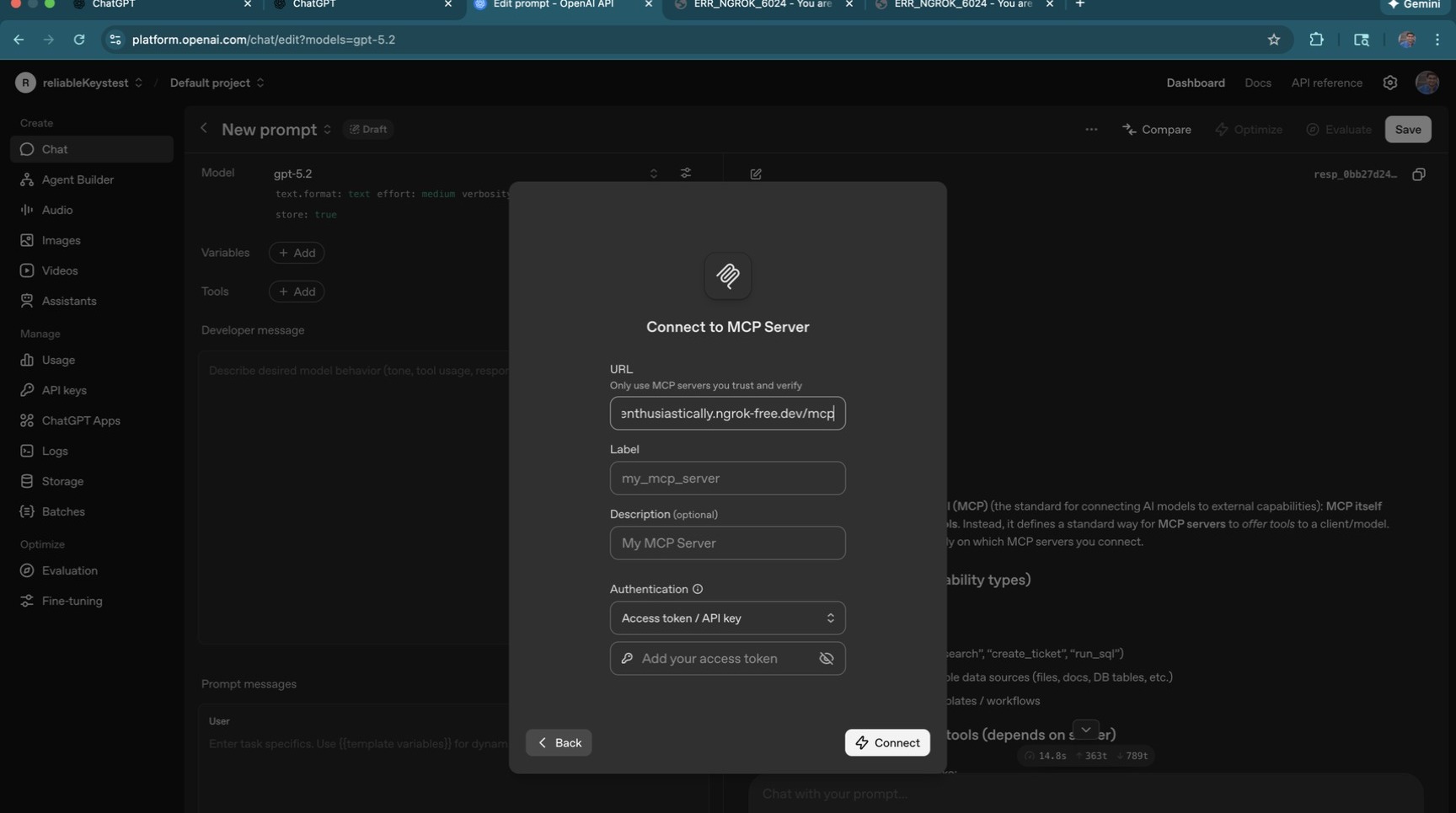
Set the server label.
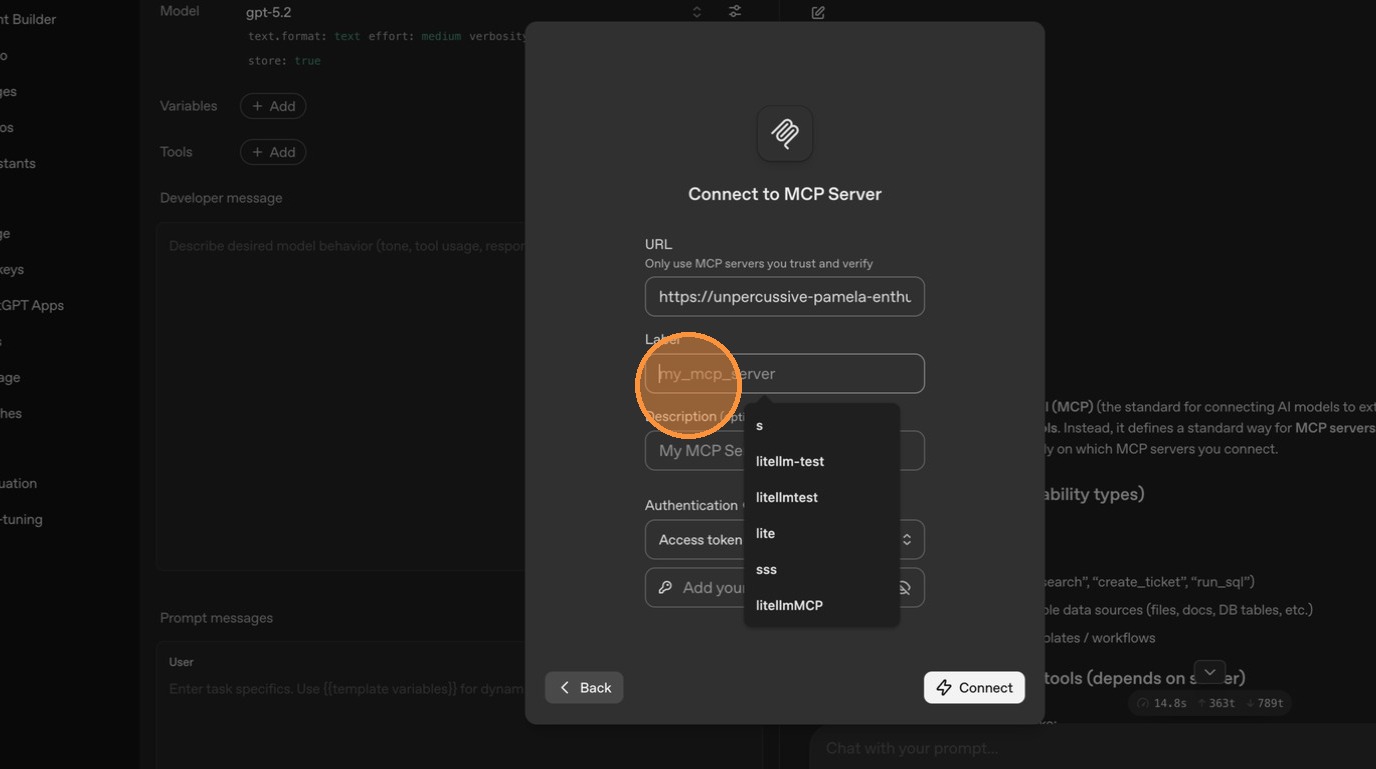
Enter your API key for authentication.
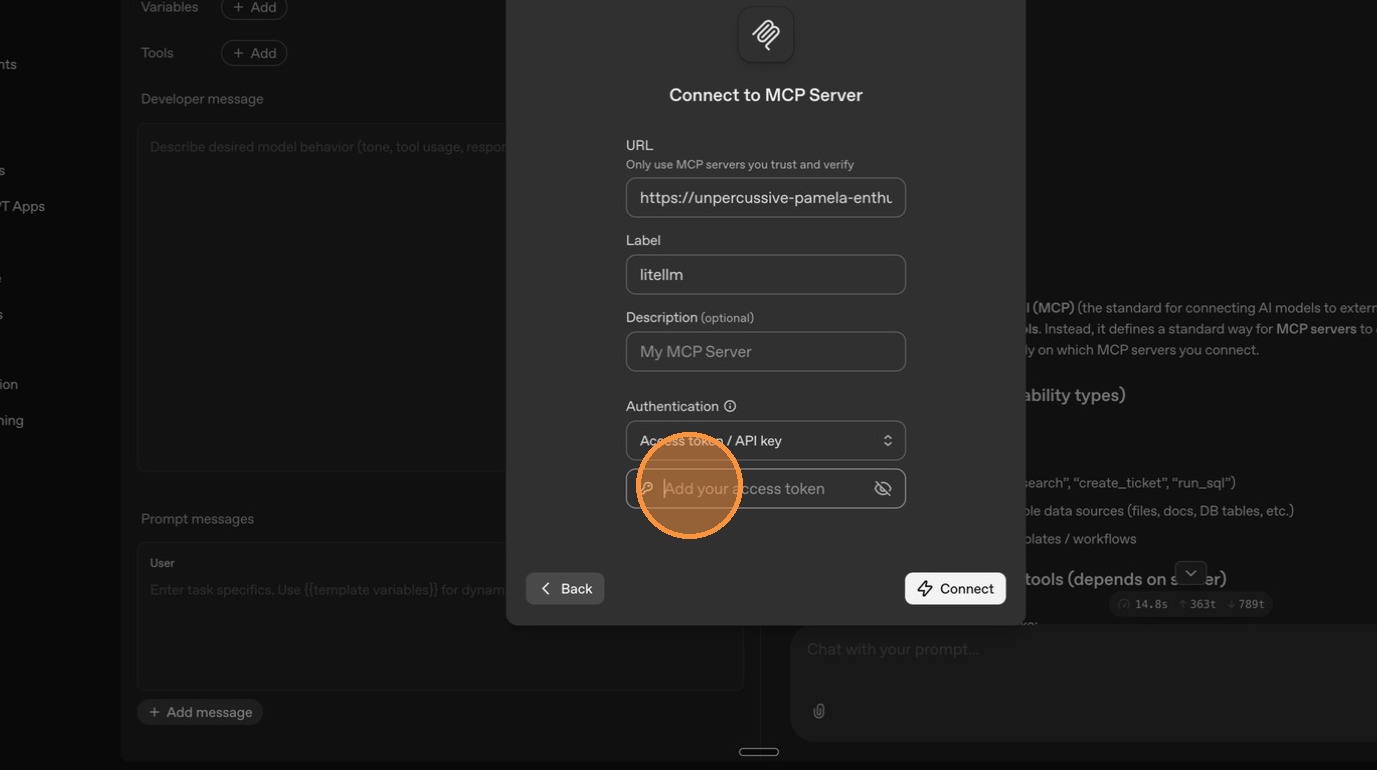
Click "Connect" to re-establish the connection.
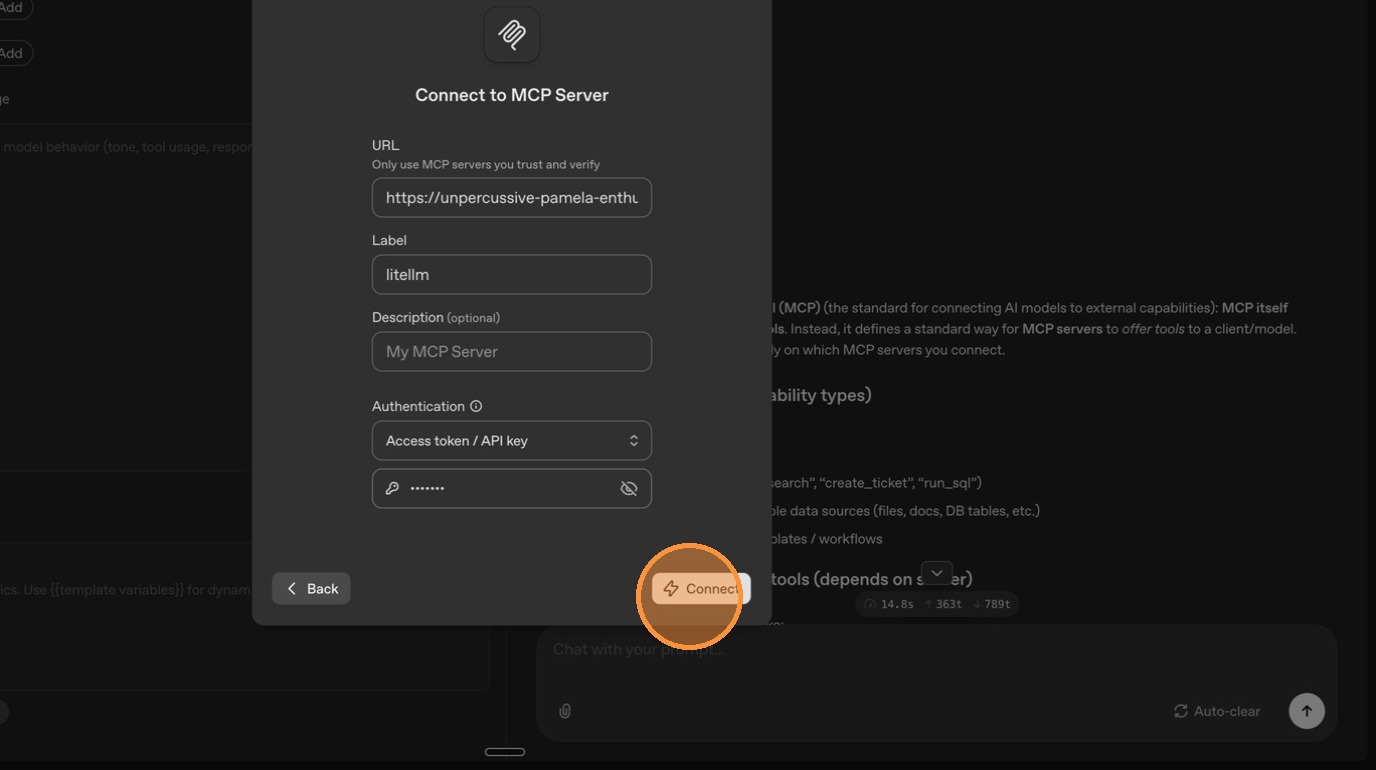
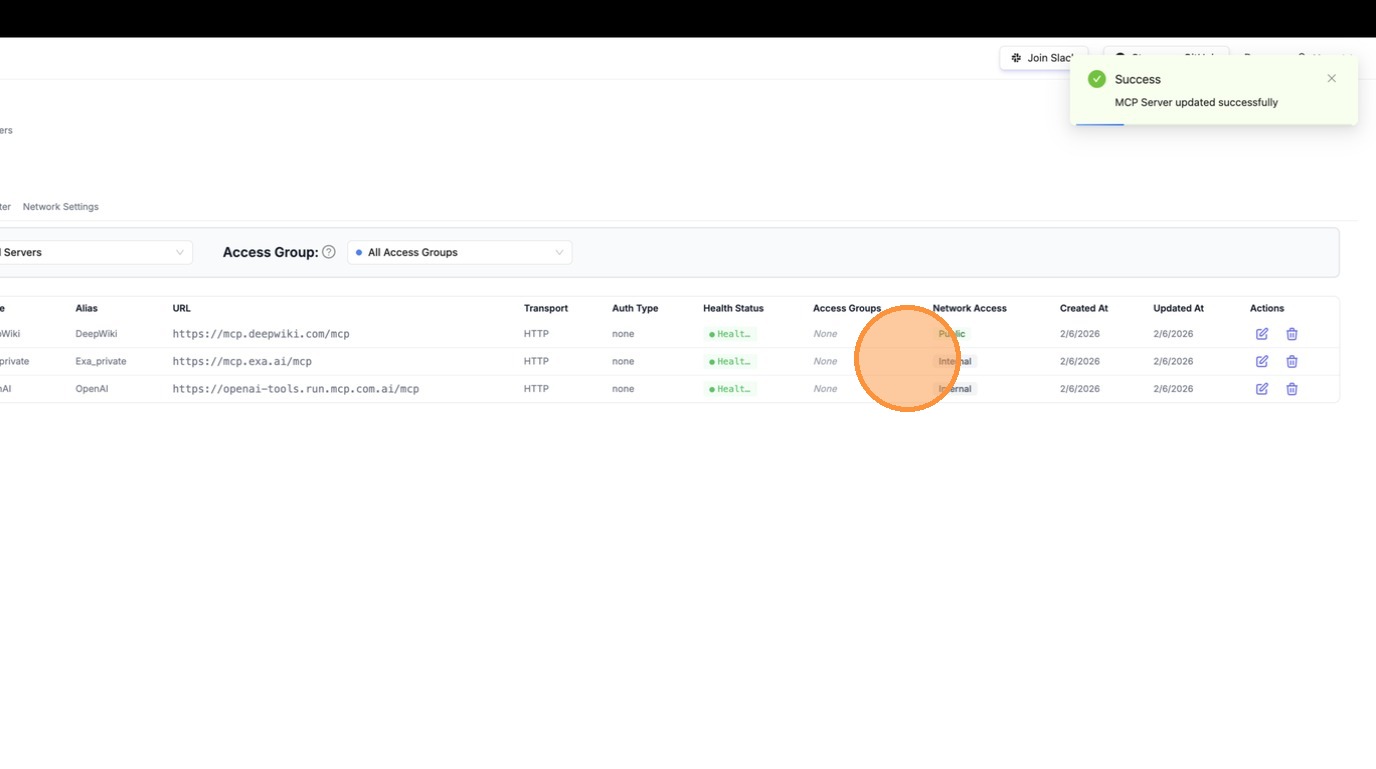
This time, only DeepWiki's tools appear — Exa is gone. LiteLLM detected that ChatGPT is calling from a public IP and filtered out Exa since it's no longer marked as public. Internal users on your private network would still see both servers.
Configuration Reference
Per-Server Setting
- UI
- config.yaml
- API
Toggle "Available on Public Internet" in the Permission Management section when creating or editing an MCP server.
mcp_servers:
deepwiki:
url: https://mcp.deepwiki.com/mcp
available_on_public_internet: true # visible to external callers
exa:
url: https://exa.ai/mcp
auth_type: api_key
auth_value: os.environ/EXA_API_KEY
available_on_public_internet: false # internal only (default)
curl -X POST <your-litellm-url>/v1/mcp/server \
-H "Authorization: Bearer sk-..." \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"server_name": "DeepWiki",
"url": "https://mcp.deepwiki.com/mcp",
"transport": "http",
"available_on_public_internet": true
}'
curl -X PUT <your-litellm-url>/v1/mcp/server \
-H "Authorization: Bearer sk-..." \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"server_id": "<server-id>",
"available_on_public_internet": false
}'
Custom Private IP Ranges
By default, LiteLLM treats RFC 1918 private ranges as internal. You can customize this in the Network Settings tab under MCP Servers, or via config:
general_settings:
mcp_internal_ip_ranges:
- "10.0.0.0/8"
- "172.16.0.0/12"
- "192.168.0.0/16"
- "100.64.0.0/10" # Add your VPN/Tailscale range
When empty, the standard private ranges are used (10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12, 192.168.0.0/16, 127.0.0.0/8).